Heart of Herbs



Swiss Alpine herbs are the heart of Ricola. Explore our universe of natural flavors – from careful cultivation to the unique taste experience of our drops melting on your tongue.
The Original 13-Herb Blend
Almost 100 years ago, Swiss confectioner Emil Richterich set out to craft a beneficial, delicious drop from herbal extracts. Fascinated by their beneficial impulses and characteristic flavors, he created the distinctive blend that remains the essence of Ricola drop to this day.
The Way to Our Herbal Drops
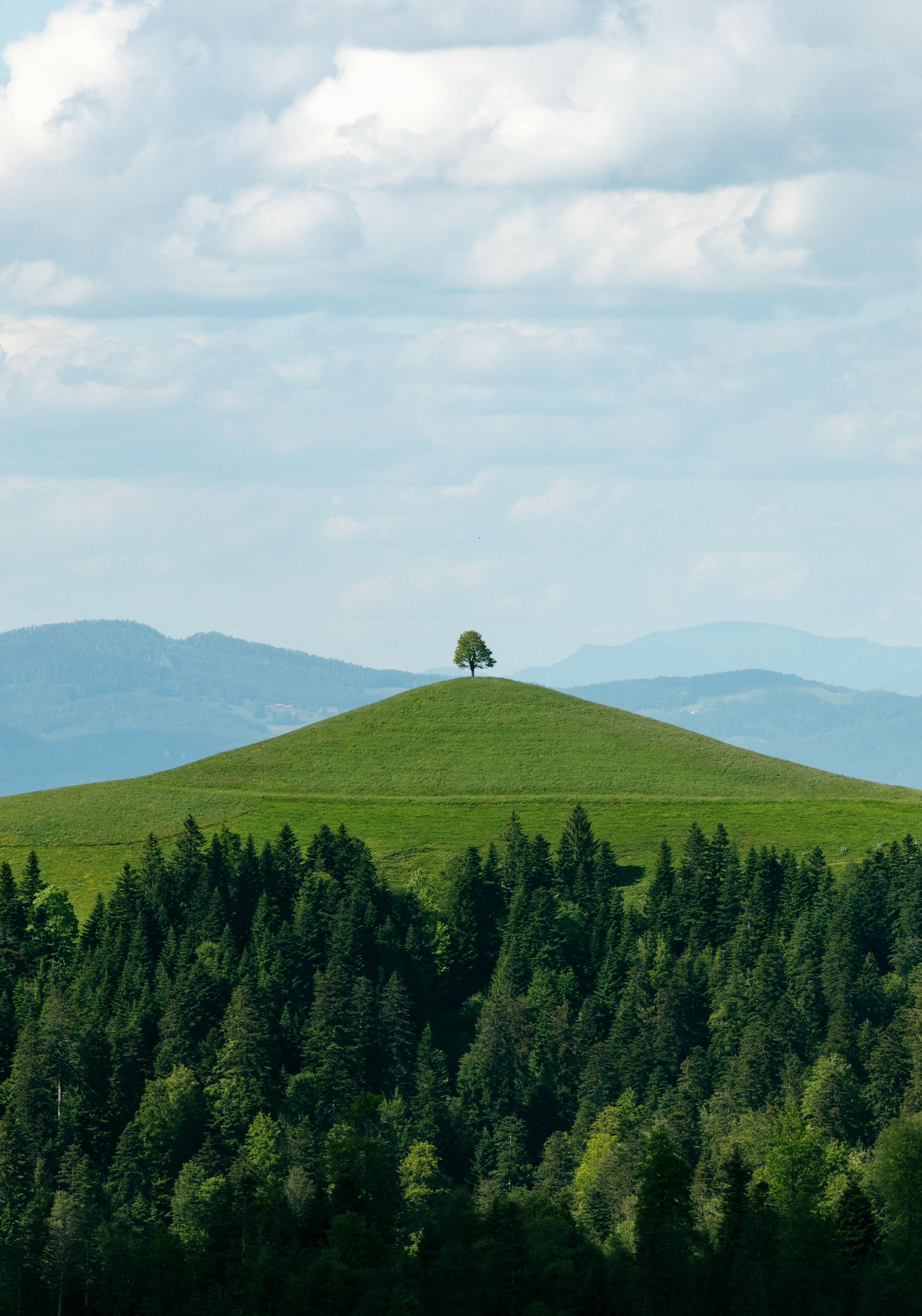
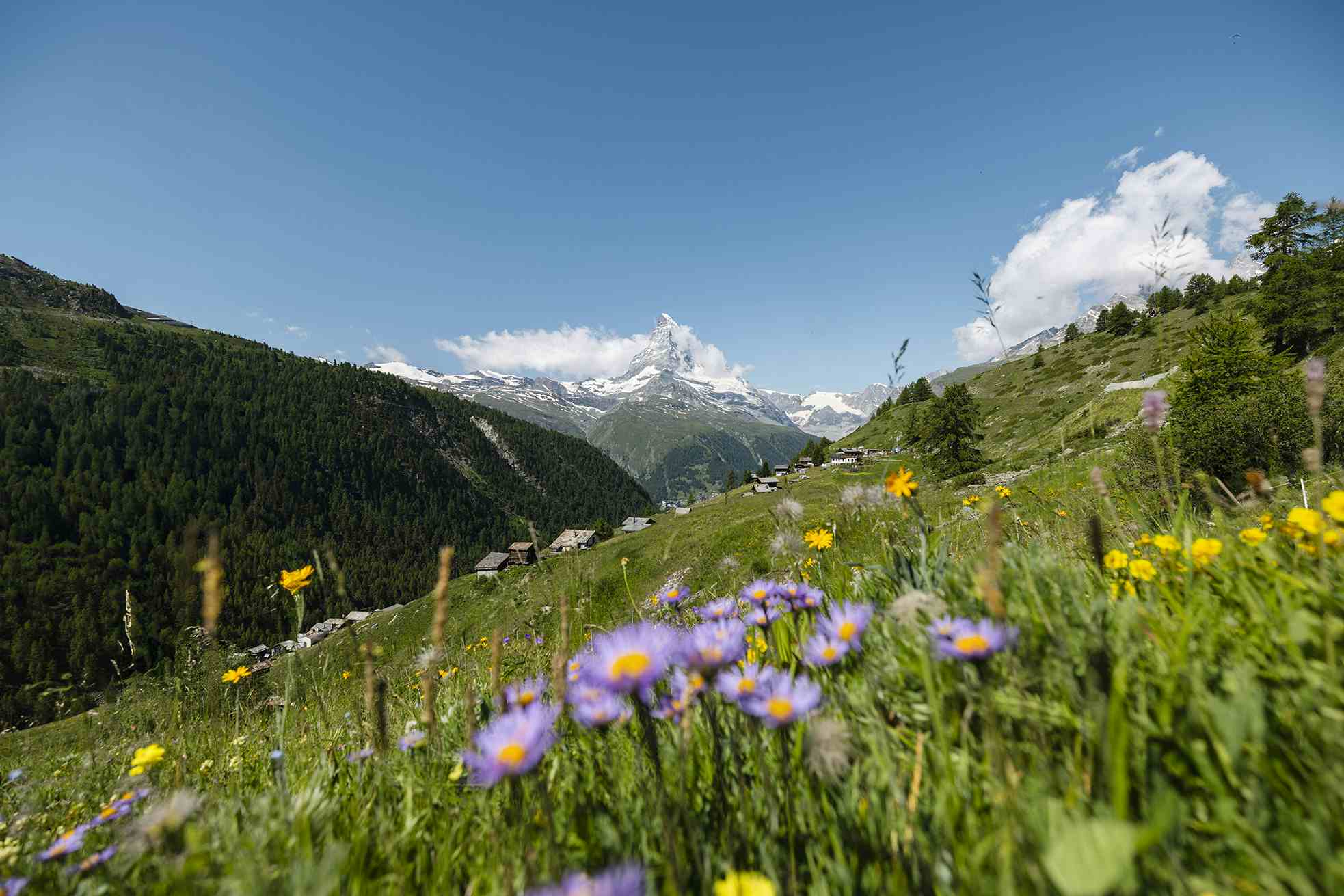
Ideal Growing Conditions
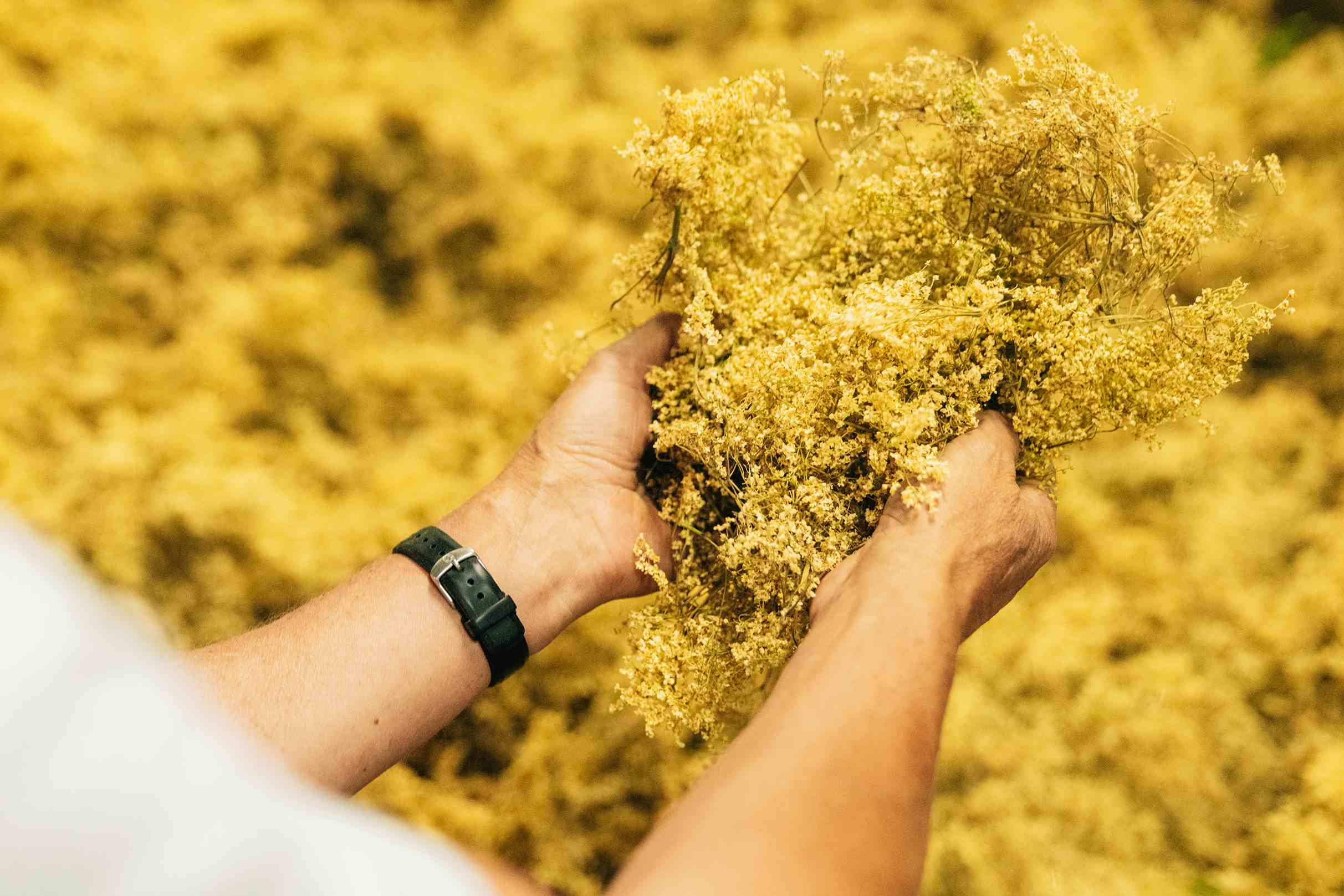
In Switzerland, each of our herbs finds an ideal growing area, far from industry and traffic. In higher regions, the sparse mountain soil and the cycle of warm days and cool nights create natural conditions that support the plants in developing exceptional purity and strength.

Dedicated Cultivation Practices
Our experienced cultivation partners grow their herbs with dedication and attention. They practice sustainable crop rotation and avoid synthetics so to maintain the organic soil's fertility. The herbs are harvested when they reach their peak of valuable ingredients.

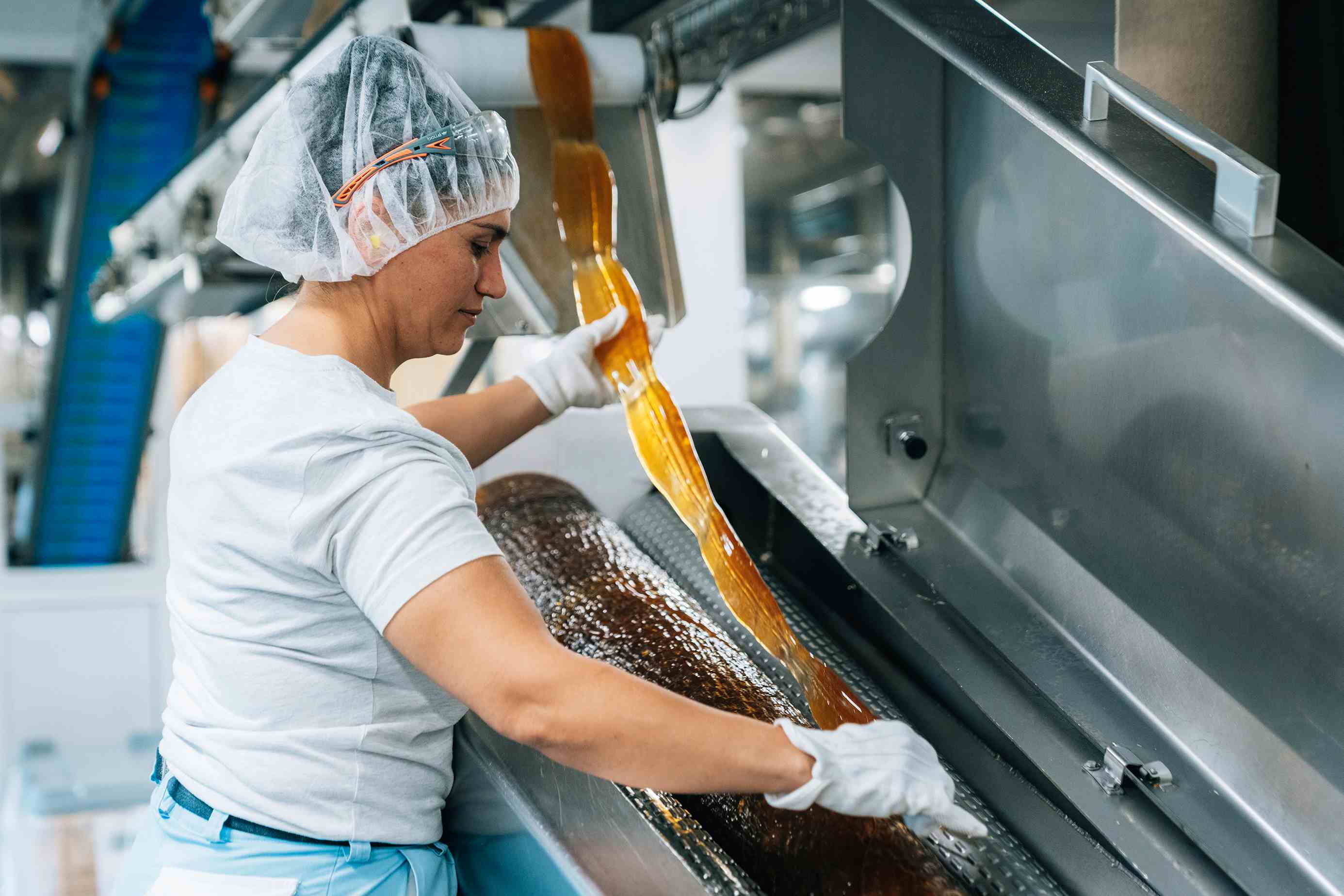
The Ricola Process
At Ricola, the freshly harvested herbs are gently dried, cleaned, and cut. We then blend them in a precise balance before extracting their special flavors and active properties through our exclusive process. This crafts the iconic 13-herb extract, the core of Ricola products.